Use a Probability Curve to Describe a Population
Namely μ is the population true mean or expected value of the subject phenomenon characterized by the continuous random variable X and σ 2 is the population true variance characterized by the continuous random variable X. Describe the conditions necessary for inference.

Understanding Probability Distributions Statistics By Jim
Check the conditions necessary for inference.
. Perform a one-sample t test. Suppose for example that we sample 100 first-graders. N is the total number of units to be sampled N is number of units in the total population.
Construct and interpret a one-sample t confidence interval. The term bell curve is used to describe a graphical depiction of a normal probability distribution whose underlying standard deviations from the mean create the. You can also use the probability distribution plots in Minitab to find the greater than.
Access answers to hundreds of statistics and probability. The graph of the distribution the equivalent of a bar graph for a discrete distribution is usually a smooth curve. Describe the properties of the normal distribution.
Posterior probability is a type of conditional probability in Bayesian statisticsIn common usage the term posterior probability refers to the conditional probability of an event given which comes from an application of Bayes theorem Because Bayes theorem relates the two conditional probabilities and and is symmetric in and the term posterior is somewhat. We use the symbol. Consider choosing a systematic sample of 20 members from a population list numbered from 1 to 836.
If the normal distribution is uneven with a skewness greater than zero or positive skewness then its right tail will be more prolonged than the left. In connection with the t distribution calculator a cumulative probability refers to the probability that a t statistic or a sample mean will be less than or equal to a specified value. The graph of the normal probability distribution is a bell-shaped curve as shown in Figure 73The constants μ and σ 2 are the parameters.
Describe the robustness of the t procedures. Describe the t distributions. Plotting net benefit against threshold probability yields the decision curve.
Visualization is also a tool for exploration that may provide insights into the data that lead to new discoveries. Understanding a Bell Curve. A typical example is seen in Fig.
A statistical population can be a group of existing objects eg. Normal curve with a mean of 70 and the area between 60 and 90 shaded. To find k divide 836 by 20 to get.
Read more is 0 the data is perfectly symmetrical. Perform the sign test to determine whether the two population locations differ. The term bell curve is used to describe a graphical depiction of a normal probability.
In statistics a population is a set of similar items or events which is of interest for some question or experiment. A cumulative probability is a sum of probabilities. Perform a matched-pairs t test.
Repeat part a with x 64. You can either sketch it by hand or use a graphing tool. Data visualization is a critical aspect of statistics and data science.
If the curve shifts to the right it is considered positive skewness while a curve shifted to the left represents negative skewness. Sampling design can be very simple or very complex. In the simplest one stage sample design where there is no explicit stratification and a member of the population is chosen at random each unit has the probability.
Of being in the sample where. If on the other hand we assume that the likely range of p t in the population is between 20 and 30 we would use the model because it. Predicting probabilities allows some flexibility including deciding how to interpret the probabilities presenting predictions with uncertainty and providing more nuanced ways to evaluate the skill of the model.
The set of all stars within the Milky Way galaxy or a hypothetical and potentially infinite group of objects conceived as a generalization from experience eg. Chapter 7 Data Visualization with ggplot. Visualization is crucial for communication because it presents the essence of the underlying data in a way that is immediately understandable.
22The curve is described by an equation or a function that we call f yThis equation is often called the probability density and corresponds to the p y we used for discrete variables in the previous section see additional discussion. The set of all possible hands in a game of poker. Instead of predicting class values directly for a classification problem it can be convenient to predict the probability of an observation belonging to each possible class.
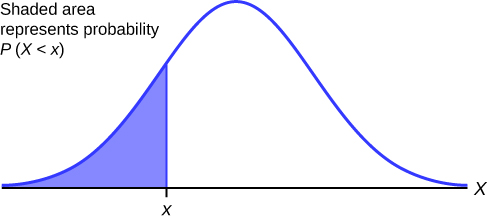
We describe decision curve analysis. The curve is called the probability density function abbreviated as pdf.

6 5 1 What Do We Mean By Normal Data
The Normal Distribution A Probability Model For A Continuous Outcome
Comments
Post a Comment